According to Chainalysis’s 2024 Crypto Crime Report, privacy coins are facilitating the proliferation of child sexual abuse material (CSAM).
The report underscores crypto’s increasing utilization as a means of payment among dark web vendors involved in CSAM.
Similar to other items available on the dark web, CSAM is frequently traded using Bitcoin.
However, the privacy-focused cryptocurrency Monero (XMR) is now playing an expanding role in illicit activities.
As per the report, many vendors of CSAM have embraced Monero, although data indicates that the coin is primarily utilized in the money laundering process after vendors have received their proceeds, rather than in the initial transactions.
The usage of Monero-friendly instant exchangers by CSAM vendors has notably surged in recent years.
Instant exchangers serve as non-custodial platforms allowing rapid conversion of one cryptocurrency into another while concealing the transaction details.
The absence of Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements makes instant exchangers convenient tools for money laundering, providing vendors with a means to acquire Monero, a privacy coin that obfuscates the destination of funds.
While centralized exchanges (CEXes) traditionally receive the bulk of illicit cryptocurrency funds from various criminal activities, among vendors dealing in child sexual abuse material (CSAM), the accessibility of instant exchangers for converting Bitcoin proceeds into Monero is narrowing this gap.
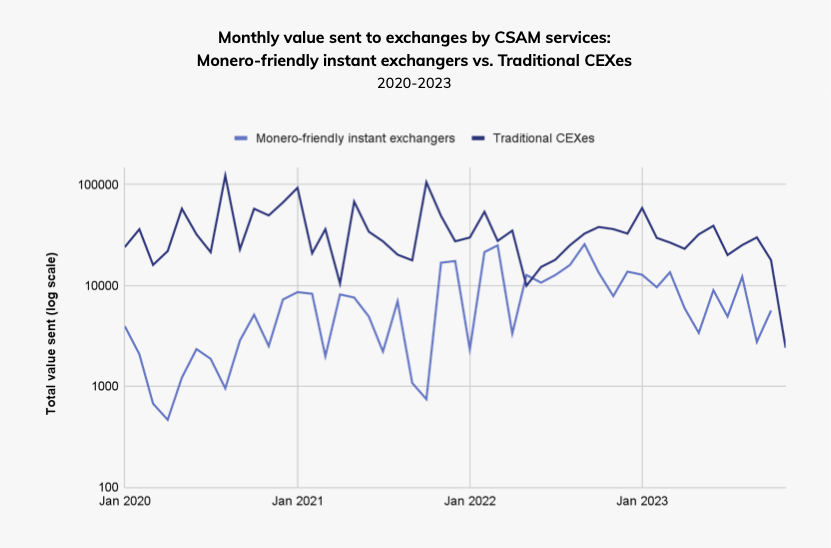
The CSAM segment of Chainalysis’s report concludes with the statement: “If the utilization of Monero-friendly instant exchangers by CSAM vendors does indeed align with the actual adoption of Monero, the data implies that Monero could be prolonging the longevity of these CSAM vendors.”
Privacy Coins and Money Laundering: The Impact of Lax KYC Protocols
The lax Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols associated with privacy coins serve as a crucial facilitator for money laundering activities within the cryptocurrency space. Unlike traditional financial institutions, which are subject to stringent KYC regulations requiring customers to verify their identities, privacy coins often operate with minimal or no KYC requirements, allowing users to transact anonymously.
This anonymity feature makes privacy coins highly attractive to individuals and entities seeking to obscure the origins and destinations of their funds. By leveraging privacy coins like Monero, users can conduct transactions without revealing personal information, such as their identity or the source of their funds. This anonymity extends to both the sender and recipient of the transaction, making it challenging for law enforcement agencies and regulatory bodies to trace illicit activities.
Furthermore, privacy coins’ lax KYC policies create a conducive environment for money laundering schemes to thrive. Criminal actors exploit the anonymity provided by privacy coins to launder proceeds from illegal activities, such as drug trafficking, cybercrime, and fraud. They may use privacy coins to convert illicit funds into digital assets with a perceived higher degree of anonymity, thereby obfuscating the illicit origins of the funds.
Despite the potential benefits of privacy coins in safeguarding users’ financial privacy, their lax KYC measures pose significant challenges for regulatory compliance and law enforcement efforts. Policymakers and regulatory authorities face the ongoing task of balancing the need to protect individuals’ privacy rights with the imperative to prevent illicit financial activities facilitated by privacy coins. This delicate balance underscores the importance of implementing robust regulatory frameworks that strike a balance between privacy protection and combating financial crime.



