summary
- Apple asserts that its latest technology is designed to withstand emerging threats posed by quantum computers by generating new keys whenever previous ones are compromised.
- The PQ3 technology, as described by Apple, ensures the generation of a unique key in a manner that cannot be duplicated if another key is compromised.
- The availability of this technology from Apple may take some time, as it has initially been integrated solely with its iMessage application.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the emergence of quantum computing presents both opportunities and challenges. While quantum computers promise unprecedented computational power, they also pose a significant threat to traditional encryption methods, potentially compromising the security of sensitive data, including cryptocurrency holdings. Recognizing this concern, tech giant Apple has recently unveiled its quantum-resistant technology, aiming to bolster the security of crypto wallets and other digital assets.
Advancements in Apple’s Quantum-Resistant Technology: Fortifying Cybersecurity Against Emerging Threats
Apple’s latest technological innovation represents a significant advancement in the realm of cybersecurity, particularly in the face of emerging threats posed by quantum computing. With the advent of quantum computers, traditional encryption methods face unprecedented challenges due to the exponentially increased computational power they offer, potentially rendering conventional cryptographic techniques obsolete.
In response to this looming threat, Apple has unveiled a groundbreaking solution aimed at fortifying digital security against quantum-enabled attacks. Central to this innovation is the ability to generate new cryptographic keys dynamically, a proactive measure designed to mitigate the vulnerabilities inherent in static key-based encryption systems.
By dynamically generating fresh keys in response to compromised ones, Apple’s technology ensures that encrypted data remains resilient against the formidable computational capabilities of quantum computers. This dynamic key generation mechanism represents a paradigm shift in encryption strategy, offering a proactive defense against the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Advancing Security: Apple’s Quantum-Resistant Technology in iMessage
Apple’s innovative technology, first implemented in iMessage, introduces a crucial security feature by replacing compromised encryption keys with entirely new ones. Unlike conventional systems where a single compromised key could potentially compromise all messages in a conversation, Apple’s dynamic key generation ensures that each message remains secure even if one key is compromised. This proactive approach to key management enhances security and mitigates the risks associated with cryptographic vulnerabilities.
The assertion that Apple’s technology is quantum-resistant is particularly noteworthy in the context of the growing threat posed by quantum computers. Quantum computing presents a paradigm shift in computational power, capable of solving complex problems that traditional computers struggle with. For instance, tasks such as breaking encryption algorithms like RSA or Elliptic Curve cryptography, which are currently considered secure, could become feasible for quantum computers.
However, despite the theoretical potential of quantum computers to break encryption, practical implementations remain elusive. As of now, no quantum computers exist on a commercial scale capable of executing such attacks. Nevertheless, the emergence of quantum computing underscores the urgency for robust cryptographic solutions capable of withstanding future threats. Apple’s proactive stance in developing quantum-resistant technology demonstrates a commitment to staying ahead of evolving cybersecurity challenges and ensuring the integrity of user data in an increasingly digital world.
However, this landscape could soon undergo a transformation. In the past year, IBM unveiled ten operational quantum computing initiatives with the capability to breach conventional encryption techniques. Such advancements could compromise private cryptographic keys, including those stored on devices like iPhones. A scientific study published in Nature in 2023 corroborated that quantum advancements indeed present novel threats to blockchain infrastructure.
“The advent of quantum computing constitutes a new paradigm in which digital technologies will endure both challenges and opportunities. Threats will come up in a variety of forms, especially when robust quantum computers will be able to break several important cryptographic algorithms currently used. Blockchain, as a
technology that strongly relies on cryptography, is not safe from these threats,” said Marcos Allende, et al.
The tech behemoth has at last devised a method to stabilize qubits, the elemental units of data storage in quantum computing. This breakthrough has opened avenues for a fresh array of algorithms, which diverge fundamentally from traditional binary-based computing systems in their problem-solving approach.
Apple’s PQ3 Technology: Revolutionizing Cryptographic Key Generation and Security
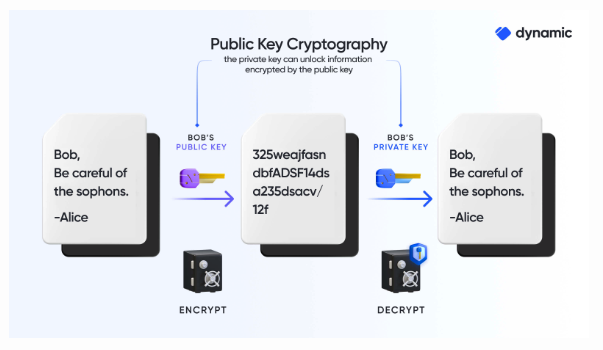
Apple’s PQ3 technology marks a significant advancement in cryptographic key generation, particularly in its ability to address the vulnerability of compromised keys. Traditional cryptographic systems often face challenges when a key is compromised, as it can potentially lead to the exposure of sensitive data or communications. However, Apple’s PQ3 technology introduces a novel approach by dynamically creating fresh keys in response to compromises, thereby enhancing security.
This dynamic key generation process ensures that each newly generated key is unique and cannot be replicated, even if another key is compromised. By generating fresh keys in this manner, Apple’s technology effectively mitigates the risk associated with compromised keys, ensuring that encrypted data remains secure and inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
Furthermore, the inability to replicate keys ensures that even if one key is compromised, it does not compromise the security of other encrypted communications or data. This proactive approach to key generation enhances the overall resilience of cryptographic systems, providing users with greater confidence in the security of their digital assets and communications.
Navigating the Future: Apple’s PQ3 Technology Rollout Strategy
While Apple’s PQ3 technology signifies a groundbreaking leap in cryptographic key generation, its widespread adoption beyond the iMessage application may require patience from users. Initially, Apple has opted to confine this innovation exclusively to iMessage, indicating that users outside this ecosystem may have to await broader integration.
Numerous factors likely contribute to Apple’s decision to confine the initial rollout to iMessage. Firstly, the tech giant may be employing a phased approach to evaluate the technology’s performance and gather user feedback within a controlled environment before extending it to other platforms. This cautious strategy ensures seamless functionality and adherence to the highest standards of reliability and security before broader deployment.
Moreover, the integration of new technologies into existing systems demands meticulous testing and optimization to guarantee compatibility and stability across diverse devices and operating systems. Apple’s unwavering commitment to user experience and reliability necessitates a gradual rollout to fine-tune the technology and address potential issues or challenges.
Strategically, Apple could be leveraging the exclusivity of PQ3 technology to bolster the appeal of its iMessage platform, enticing users to remain within the Apple ecosystem. By offering cutting-edge security features unavailable on rival platforms, Apple aims to differentiate its products and services while enriching the user experience.