Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum, recently shared details about the upcoming stages of the protocol’s simplification endeavor, known as “The Purge.”
The primary objective of this initiative is to streamline the Ethereum protocol by minimizing the storage demands for historical data. This will alleviate the strain on node operators’ storage resources and substantially reduce the technical complexities associated with the protocol.
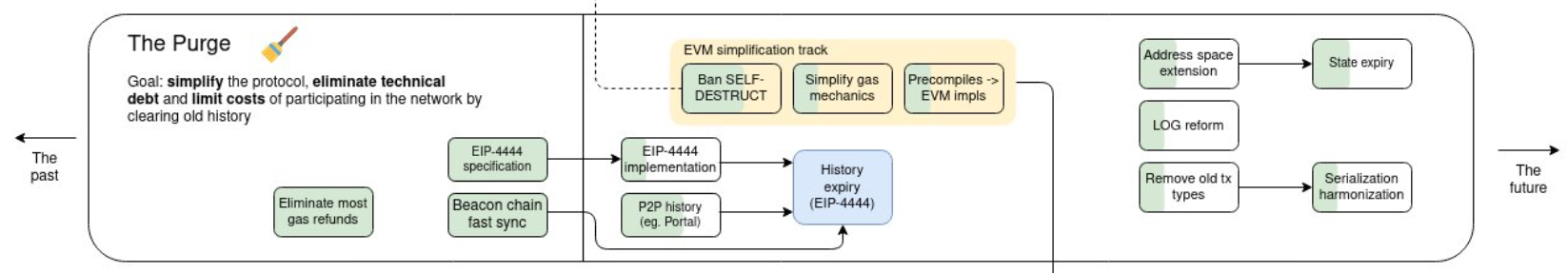
In essence, “The Purge” project aims to trim down Ethereum and tackle the accumulated technical challenges. Buterin’s announcement suggests the presence of further Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) with similar aims of simplification.
Vitalik Buterin, a prominent figure behind Ethereum, introduces “The Purge” initiative aimed at streamlining the blockchain protocol.
A quick note on next steps in Ethereum protocol simplification and node resource load decreases (aka "the Purge"):https://t.co/BAebCGrisB
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) April 1, 2024
In a recent report, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin shed light on the successful implementation of Ethereum Improvement Protocol (EIP)-6780 during the Dencun hard fork. This significant milestone marked a pivotal moment in the evolution of the Ethereum protocol, as it brought about substantial simplification measures and bolstered security protocols.
One of the standout changes post-EIP-6780 implementation is the revision of the “SELFDESTRUCT” code, a crucial aspect of Ethereum’s functionality. This revision aimed to streamline the protocol by limiting the number of storage slots that could be edited in a single block. This limitation was roughly determined by the gas limit divided by 5000, a move that aimed to optimize efficiency and enhance security measures within the Ethereum network.
Buterin’s optimism shines through as he anticipates the implementation of future EIPs that will build upon the foundation laid by EIP-6780. These forthcoming improvements are expected to further refine Ethereum’s functionality by potentially eliminating the SELFDESTRUCT function altogether. Such enhancements not only promise to fortify the network’s security but also pave the way for greater efficiency and scalability in Ethereum’s operations.
 Source: Vitalik Buterin
Source: Vitalik Buterin
Referred to as “The Purge” by Buterin, this initiative encompasses a thorough cleanup endeavor within the Geth Ethereum client, targeting the removal of redundant code post the transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS). Recent Ethereum Improvement Proposals have also played a role in enhancing how vacant accounts are managed, thereby boosting overall code efficiency.
One of the key objectives of “The Purge” is to optimize data storage on the Ethereum blockchain. EIP-4444, introduced during the Dencun upgrade, introduces the concept of “blobs” for specific data storage, thereby reducing long-term storage requirements and facilitating smoother node participation. Additionally, the proposal suggests automating the removal of older blocks after a designated time, further trimming down storage needs.
Buterin underscores that “The Purge” will enhance Ethereum’s node decentralization by dispersing historical data more efficiently across the network. While acknowledging that not all nodes will store complete historical data, efforts are underway to explore solutions such as block explorers and decentralized peer-to-peer networks to ensure accessibility.
Moreover, “The Purge” encompasses plans to assess and optimize precompile Ethereum contracts and introduce a novel data structure called SimpleSerialize (SSZ) to replace the existing block structure. This move is aimed at simplifying data usage and development processes, thereby contributing to Ethereum’s ongoing evolution and efficiency.
Vitalik expresses apprehension regarding intricate Layer 2 scaling solutions
On December 30, 2023, Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum, provided a comprehensive update on the Ethereum roadmap, shedding light on notable advancements in Surge, particularly in rollup scaling initiatives such as EIP-4844. This update underscored the continuous development and refinement of rollup technologies, which play a pivotal role in Ethereum’s scalability solutions.
Moreover, Buterin emphasized the imperative of long-term enhancements in cross-rollup standards and interoperability. These improvements are crucial for fostering a more robust and interconnected Ethereum ecosystem, allowing different rollup solutions to seamlessly interact and collaborate. Such interoperability is essential for ensuring the scalability and sustainability of Ethereum in the face of growing demand and evolving technological landscapes.
Honestly I'm about 3x less confident in the "simplify L1 even at the expense of more complicated L2s" concept than I was five years ago. The challenge is that when you can trade off between L1 bug risk and L2 bug risk, it's not actually clear that the latter is better!
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) February 21, 2024
Recently, Buterin expressed reservations regarding the growing complexity of Layer 2 scaling solutions within blockchain ecosystems. Through social media channels, he highlighted potential risks associated with intricate Layer 2 networks and advocated for a more balanced development approach.
In the blockchain community, there’s a prevailing notion that Layer 1 networks should prioritize simplicity to minimize the likelihood of critical bugs and vulnerabilities. This approach delegates the implementation of more complex features to Layer 2 networks, which specialize in providing scalable solutions.
Buterin underscored the seriousness of critical bugs within Layer 2 networks, emphasizing that while Layer 1 blockchains can swiftly recover from consensus failures, similar failures in Layer 2 could result in permanent loss of user funds. He cautioned against the escalating complexity of Layer 2 solutions and the inherent risks they carry.
Proposing an alternative strategy, Buterin suggested enhancing Layer 1 networks with sophisticated features to alleviate the burden on Layer 2 networks, thereby allowing them to maintain a reasonable level of simplicity. By reducing complexity, the likelihood of critical bugs and security vulnerabilities could be mitigated, ultimately enhancing the safety of user funds and bolstering system reliability.



